CHEMICAL REACTION EQUATION
Chemical reaction is the process in which new substances with new properties are formed from one or more substances is called Chemical Reaction.
During chemical reaction following changes has taken place:-
(i) Change in state (ii) Change in colour
(iii) Evolution of gas (iv)Change in temperature
Reactants :- The substance which take part in chemical reactions are called Reactants.
Reactant --- on the left-hand side
Products :- The substance which are formed in a chemical reaction are Called Products.
Product --- on the right-hand side.Ways of Representing a chemical Reaction :-

Chemical Equation :- A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formula.

In a Balanced chemical equation :- the number of atoms of different elements on both side of the equation (Reactant and Product side) is always equal.
Eg. :-


TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS:-
1)COMBINATION REACTION:- The reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
OR
It is a reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is known as a combination reaction.
e.g. :-

Slaked lime is used for white washing walls.
Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls.

Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days of white washing and gives a shiny finish to the walls.

Exothermic Reactions:- Reaction in which heat is released along with formation of products.
e.g. :-
Thermal decomposition:-When decomposition is carried out by heating.
e.g.,

Eg.,
Eg.,



The Substance which either gives Oxygen or removes hydrogen in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidizing agent.
Reduction :-
(i) The addition of hydrogen to substance OR
(ii) The removal of Oxygen from a substance.
Redox reaction:- A reaction in which oxidation and reduction taking place together is called a redox reaction.

In this reaction CuO is reduced to Cu and H2 is oxidized to H2O.
Carbon ( C) is a reducing agent as it undergo Oxidation.
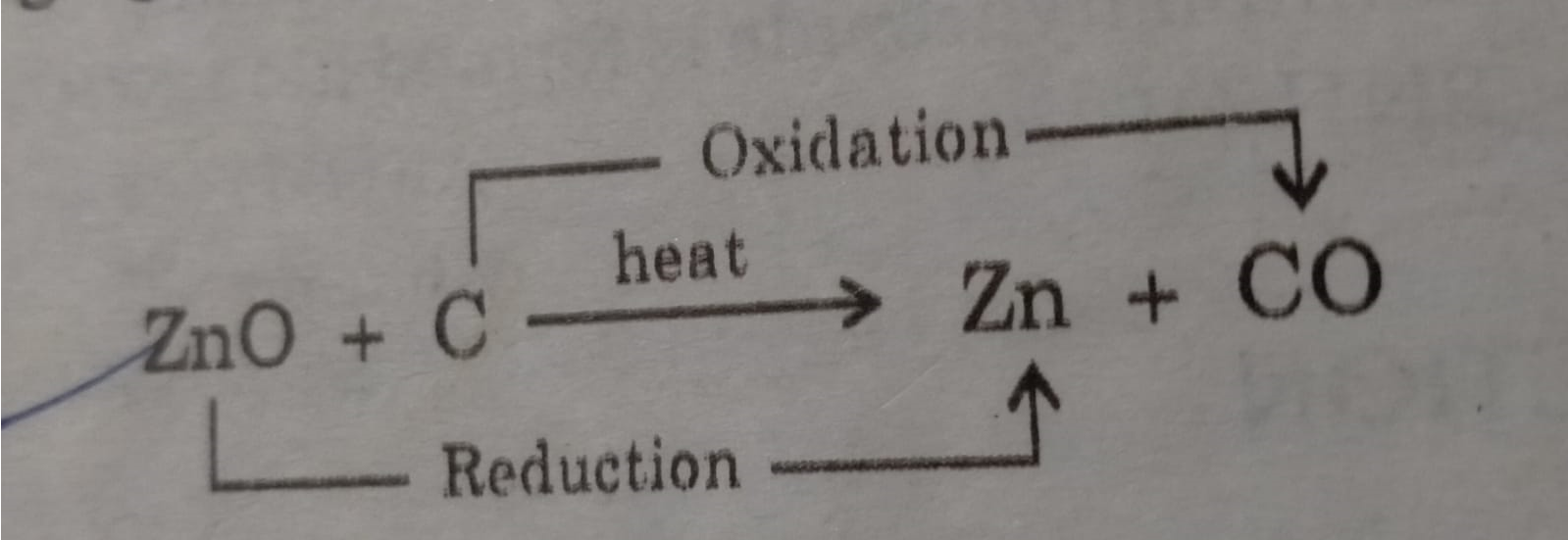
ZnO is an Oxidising agent as undergo reduction.
In this reaction ZnO is reduced to Zn and C is oxidized to CO.

HCl is a reducing agent as it undergo Oxidation.
MnO2 is an Oxidising agent as undergo reduction.
In this reaction MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2 and HCl is oxidized to Cl2.
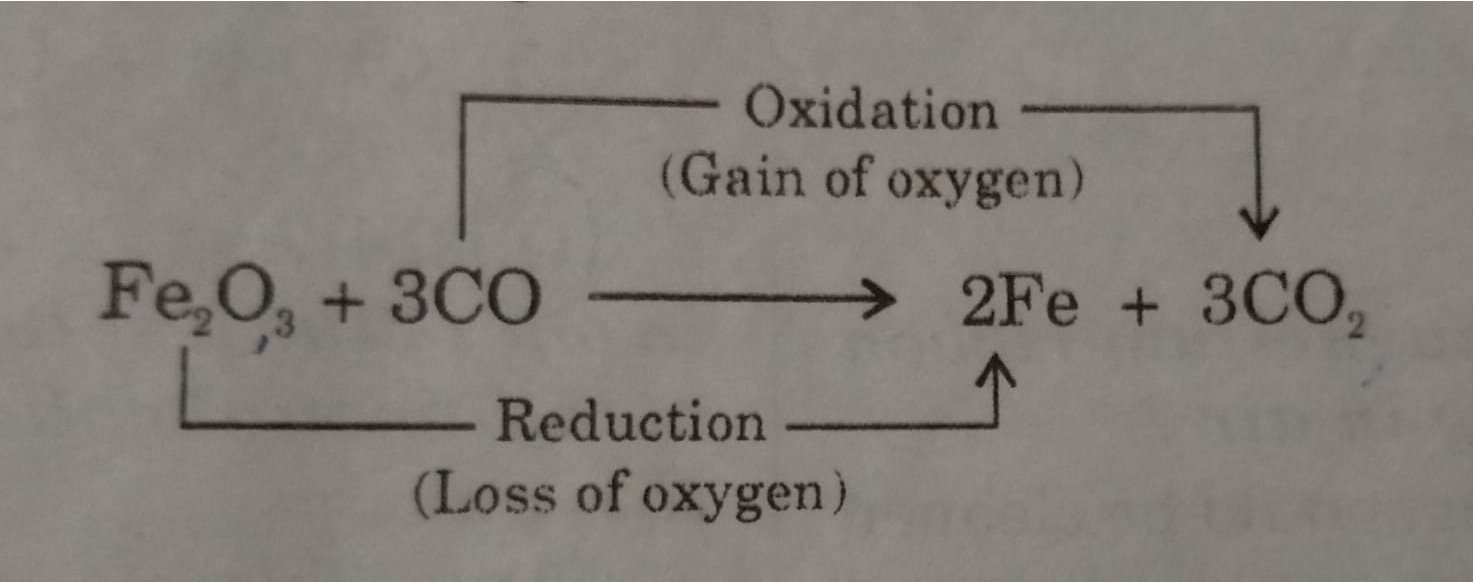
3CO is a reducing agent as it undergoes Oxidation.
Fe2O3 is an Oxidising agent as undergoes reduction.
In this reaction Fe2O3 is reduced to 2Fe and 3CO is oxidized to 3CO2.
Effects of Oxidation Reaction in Daily Life :-
Corrosion (rusting) weakens the iron and steel objects and structures such as railings, car bodies, bridges and ships etc. and cuts short their life.
Methods to Prevent Rusting:-
• By painting.
• greasing and oiling.
• galvanization
• electroplating
Corrosion of Copper: Copper objects lose their lustre and shine after some time because the surface of these objects acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate Cuco3.Cu(OH) 2 when exposed to air.
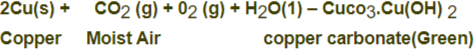
Corrosion of Silver Metal:- The surface of silver metal becomes dull on exposure to air, due to the formation of a coating of black silver sulphide (Ag2 S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
(i) By adding antioxidants
(iii) Replacing air by nitrogen














0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.